Scalping and swing trading are two popular strategies in the forex market, employed by traders to profit from price movements in currency pairs. While both aim to capitalize on price action, they differ significantly in terms of timeframes, trading frequency, and methodologies. Here’s a detailed comparison of scalping and swing trading to help you determine which approach might be better suited to your trading style and goals.
Scalping
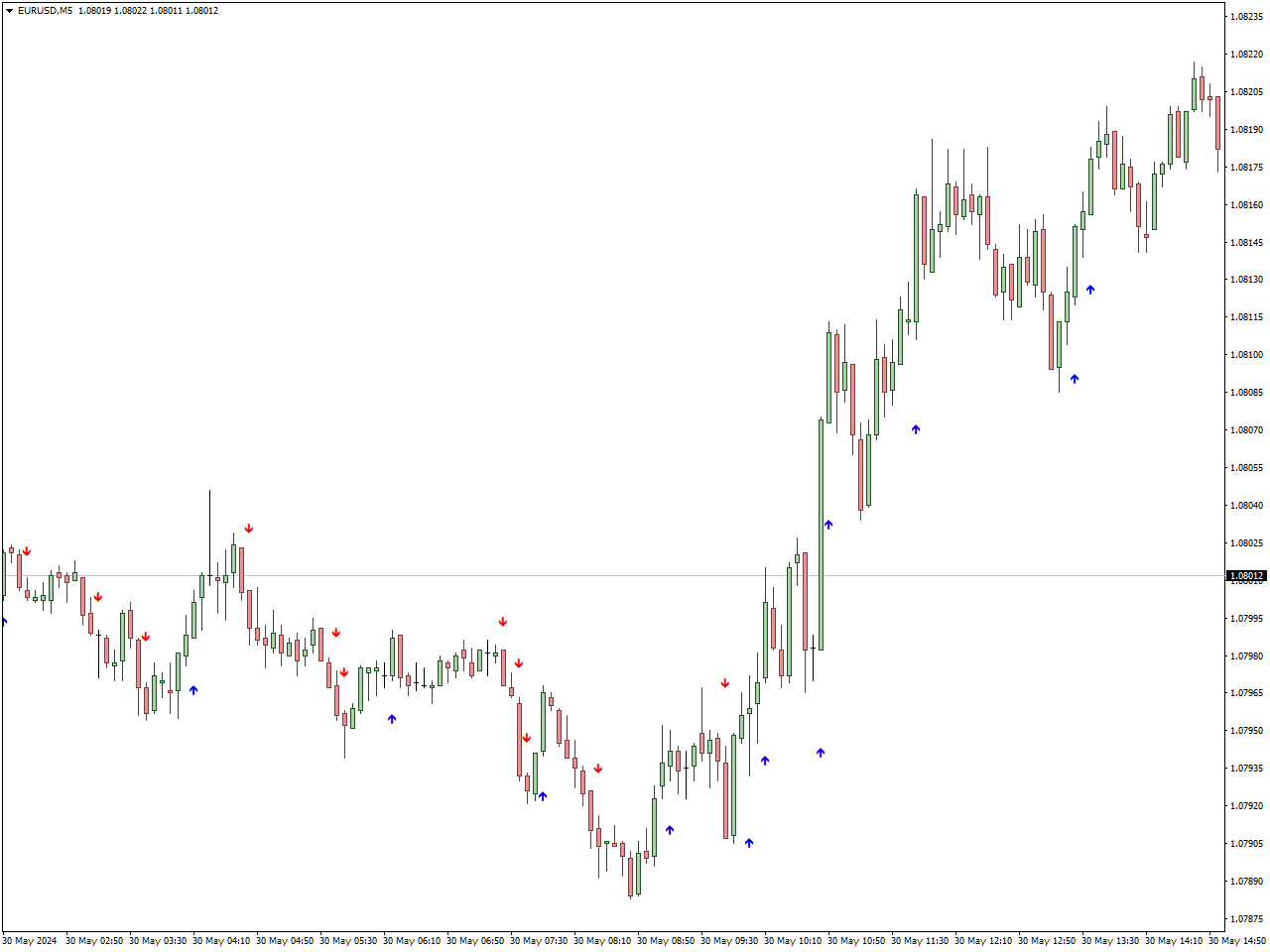
Scalping is a strategy designed to profit from very short-term price movements, often within seconds. It involves executing a high volume of trades to capture small price changes, requiring constant market monitoring and rapid decision-making. Scalping offers the potential for consistent, small profits throughout the trading day but demands a high level of commitment, expertise, and emotional resilience due to its fast-paced nature. In the example below, you can see the Best Scalping Indicator in action.
Key Characteristics:
Timeframe: Scalping involves holding positions for very short periods, typically for a few minutes. This approach requires traders to act quickly to exploit small price movements measured in pips.
Trading Frequency: Scalping involves a high frequency of trades, often hundreds of transactions in a single day. This high activity level can lead to higher transaction costs due to spreads and commissions.
Strategies: Scalpers rely heavily on technical analysis, using indicators such as moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and stochastic oscillators to identify entry and exit points. They often use market orders for quick execution and focus on liquidity to ensure they can enter and exit trades swiftly. Candlestick charts and price charts are essential tools for scalpers to analyze market conditions and execute trades efficiently. The chart shows the EUR/USD price movements with Bollinger Bands and red arrows highlighting key points. In scalping, these arrows indicate rapid trading opportunities: touching the lower band suggests a quick buy signal (oversold), while touching the upper band indicates a fast sell signal (overbought). The Bollinger Bands help scalpers identify these crucial entry and exit points based on market volatility for short-term gains.
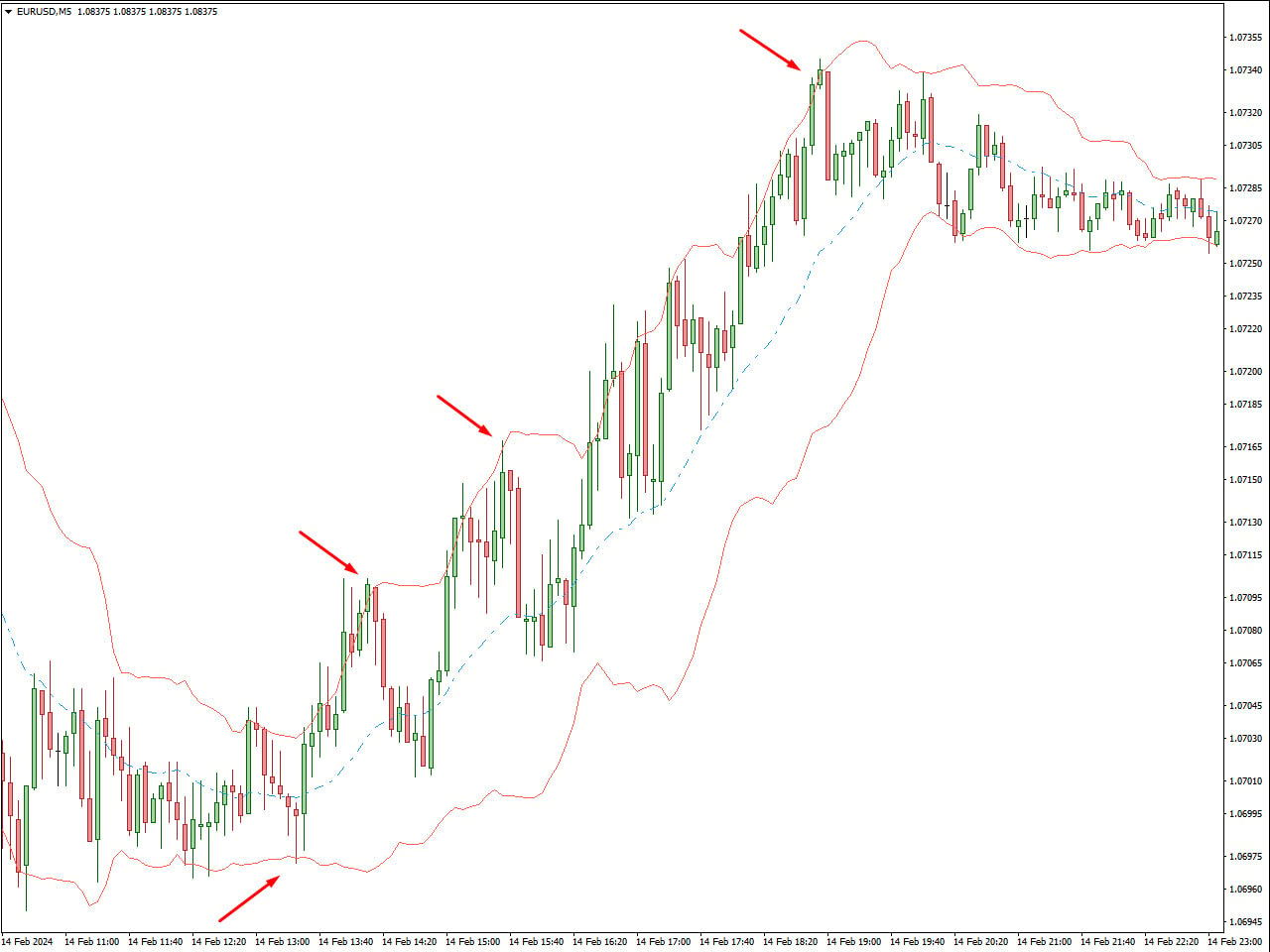
Risk and Reward: The fast-paced nature of scalping results in higher stress levels due to the need for rapid decision-making. While scalpers can accumulate frequent small profits, the strategy requires strict risk management strategies to avoid significant losses from adverse price movements. Stop-loss orders and take-profit orders are commonly used to manage risk and lock in profits.
Examples of Scalping Tools: Scalpers use tools like 1-minute and 5-minute charts, real-time price feeds, and volume indicators to identify trading opportunities. High-speed trading platforms and direct market access (DMA) are essential for executing trades quickly. Expert advisors (EAs) and automated trading software can also be used to enhance trading efficiency.
Swing Trading
Swing trading is a strategy designed to capture medium-term price movements, making it suitable for traders who cannot monitor markets continuously. It involves analyzing chart patterns, technical indicators, and trendlines to identify trade setups, with positions held overnight. Swing trading offers the potential for substantial profits from larger price swings and usually involves lower transaction costs than scalping. However, it demands patience, discipline, and a strong grasp of technical and fundamental analysis to manage overnight risks and market volatility effectively.
Key Characteristics:
Timeframe: Positions in swing trading are typically held for a few days to weeks. This approach involves less frequent trading compared to scalping, resulting in fewer transactions over the same period.
Trading Frequency: Swing trading involves a lower frequency of trades, leading to potentially lower transaction costs. Traders can take advantage of the flexibility to analyze markets and make decisions outside of regular trading hours, including during different trading sessions (Asian, London, New York).
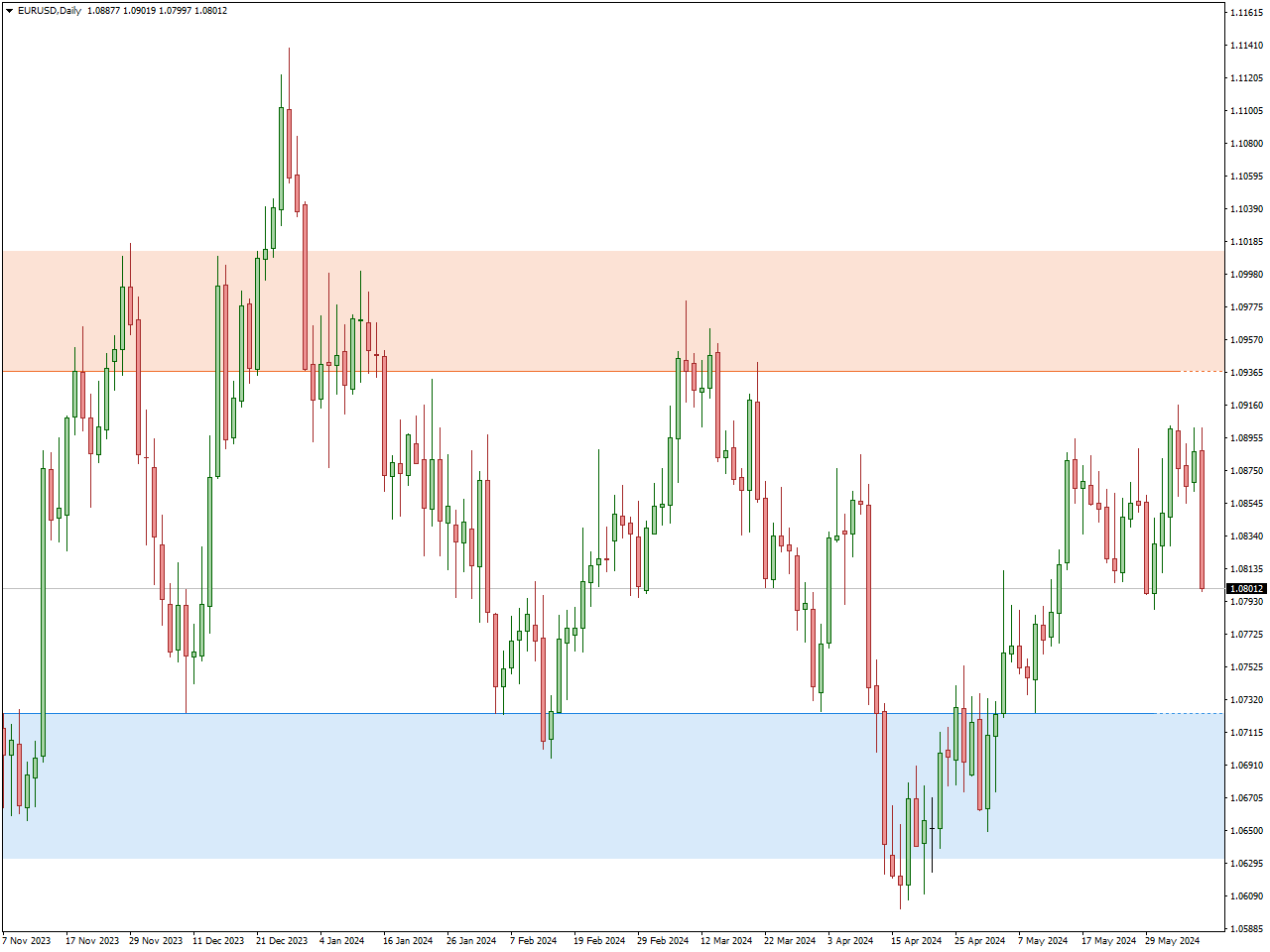
Strategies: Swing traders rely on technical analysis, using chart patterns, technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI, and MACD, and trendlines to identify potential trade setups. Additionally, they may incorporate fundamental analysis to gain insights into broader market trends and economic conditions. Identifying support and resistance levels is crucial for setting entry and exit points. Forex signals and trading signals from forex brokers can be incredibly beneficial for swing traders. These signals, which are recommendations or alerts about when to enter or exit a trade, are often generated by experienced analysts and sophisticated algorithms. By following these signals, swing traders can gain valuable insights into market trends and potential trading opportunities. In the image below, you can see the support and resistance levels provided by the FXSSI indicator.
Risk and Reward: The longer holding periods in swing trading generally lead to lower stress levels for traders. There is potential for larger individual profits due to the ability to capture more significant price swings. However, traders are exposed to overnight risk, which can be managed using stop-loss orders and take-profit orders.
Examples of Swing Trading Tools: Swing traders utilize various tools to enhance their trading decisions. Candlestick charts help identify potential reversal and continuation patterns. Swing highs and lows are crucial for anchoring technical indicators like Anchored VWAP. Additionally, indicators such as Fibonacci retracement, Bollinger Bands, and momentum oscillators are commonly used to refine trade setups. Fundamental analysis and market sentiment analysis are also important components of swing trading strategies.
Scalping vs. Swing Trading: Comparison
Time Commitment: Scalping requires constant attention and quick decision-making throughout the trading session. Swing trading, in contrast, is suitable for those who cannot dedicate their entire day to trading and prefer a more flexible schedule.
Trading Frequency: Scalping involves a high frequency of trades with higher transaction costs, whereas swing trading features a lower frequency of trades with potentially lower transaction costs.
Skill and Experience: Scalping demands significant market experience, quick reflexes, and advanced technical analysis skills. Swing trading may require less immediate market experience but still demands a strong understanding of technical and fundamental analysis.
Risk Management Strategies: Scalping requires strict discipline in managing rapid intraday price fluctuations and implementing tight stop-loss orders. Swing trading involves managing overnight risk and using stop-loss orders effectively to handle market volatility.
Market Conditions: Scalping is most effective in highly liquid markets with minimal spreads, where quick trades can capitalize on small price movements. Swing trading is more suited to stable or trending markets where price swings can be captured over days or weeks.
What should i choose?
Deciding between scalping and swing trading depends on your personal preferences, time availability, risk tolerance, and trading experience. If you prefer a fast environment and can dedicate significant time to constant market monitoring, scalping might be the best choice. Scalping requires quick reflexes, advanced technical analysis skills, and the ability to handle high-frequency trading and stress. On the other hand, if you have limited time to trade during the day and prefer a more flexible schedule, swing trading may be more suitable. Swing trading allows you to hold positions for several days to weeks, focusing on capturing larger price swings with lower transaction costs. It demands patience, discipline, and a solid understanding of technical and fundamental analysis. Assess your trading goals, lifestyle, and comfort with risk to determine which strategy aligns better with your approach to the forex market.
Conclusion
Scalping is a high-intensity trading strategy best suited for those who can commit to full-time trading and thrive in fast-paced environments. It requires significant market experience, quick reflexes, and advanced technical analysis skills. The frequent trades and need for rapid decision-making can be challenging, but disciplined risk management and a focus on liquidity can help scalpers achieve consistent small profits.
Swing trading is an excellent choice for those who prefer a more flexible schedule and lower frequency of trades. This approach allows traders to develop their skills in technical and fundamental analysis gradually, making it suitable for beginners. By using tools like forex signals and analyzing market sentiment, swing traders can make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
Ultimately, the choice between scalping and swing trading depends on your personal preferences, time availability, risk tolerance, and trading experience. By understanding the key differences and considerations, you can choose the strategy that best aligns with your trading goals and lifestyle.



